In this article, we will introduce the Entity Framework 5.0 Code First approach in MVC applications. The ADO.NET Entity Framework is an Object Relational Mapper (ORM) included with the .NET framework. It basically generates business objects and entities according to the database tables. It provides basic CRUD operations, easily managing relationships among entities with the ability to have an inheritance relationship among entities.
When using the EF we interact with an entity model instead of the application's relational database model. This abstraction allows us to focus on business behavior and the relationships among entities. We use the Entity Framework data context to perform queries. When one of the CRUD operations is invoked, the Entity Framework will generate the necessary SQL to perform the operation.
How to Implement
To create this application we should have a basic knowledge of the DbContext class of theSystem.Data.Entity namespace. We should also be familiar with views because in this article I am not describing views for each action method so you can create a view according to action methods or you can scaffold templates to create a view for Edit, List, Create, Delete and Details.
We need to install the Entity Framework Nuget package in our application. When we install the Entity Framework Nuget package, two references (System.Data.Entity and EntityFramework) are added to our application. Thereafter we can perform CRUD operations using Entity Framework.
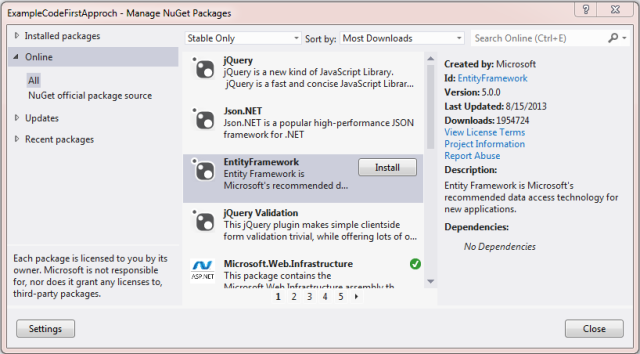
How to Use Entity Framework
Whether you have an existing database or not, you can code your own classes and properties (aka Plain Old CLR Objects, or POCOs) that correspond to tables and columns and use them with the Entity Framework without an .edmx file. In this approach the Entity Framework does not leverage any kind of configuration file (.edmx file) to store the database schema, because the mapping API uses these conventions to generate the database schema dynamically at runtime. Currently, the Entity Framework Code First approach does not support mapping to Stored Procedures. The ExecuteSqlCommand() and SqlQuery() methods can be used to execute Stored Procedures.
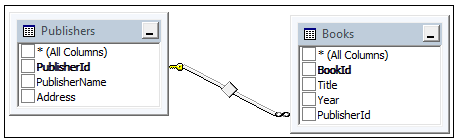
To understand the Entity Framework Code First Approach, you need to create an MVC application that has two entities, one is Publisher and another is Book. So let's see an example step-by-step. To create your MVC Application, in Visual Studio select "File" -> "New" -> "Project..." then select "MVC 4 Application" then select "Empty Application".
1. Create Modal Classes
We create classes for Publisher and Book under the Models folder, those classes are used as entities and an entities set. These classes will have mapping with a database because we are using the code first approach and these classes will create a table in a database using the DbContext class of Entity Framework. So let's see these classes one by one. The Publisher class is in the Models folder; that file name is Publisher.cs as in the following:
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace ExampleCodeFirstApproch.Models
{
public class Publisher
{
public int PublisherId { get; set; }
public string PublisherName { get; set; }
public string Address { get; set; }
public ICollection<book> Books { get; set; }
}
}</book>
The Book class is in the Models folder; that file name is Book.cs as in the following:
namespace ExampleCodeFirstApproch.Models
{
public class Book
{
public int BookId { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Year { get; set; }
public int PublisherId { get; set; }
public Publisher Publisher { get; set; }
}
}
2. Create Data Access Layer
This part of the article is the heart of the article as well as the code first approach. First of all we need a connection string so we can connect with our database by application. We create a connection in the web.configfile. I provide the connection string name as DbConnectionString, you are free to give any name to it but remember it because we will use it in our context class.
<connectionStrings>
<add name="DbConnectionString"
connectionString="Data Source=steve-PC;Initial Catalog=CodeFirst;User ID=sa;
Password=*******" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" />
</connectionStrings>
We have both classes, Publisher and Book, so now we will create a context class. We create aLibraryContext class under the Models folder, that file name is LibraryContext.cs. This class inherits DbContextso we can use the DbContext class methods using a LibraryContext class object as in the following:
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
using System.Data.Entity;
namespace ExampleCodeFirstApproch.Models
{
public class LibraryContext :DbContext
{
public LibraryContext()
: base("name=DbConnectionString")
{
}
public DbSet<Publisher> Publishers { get; set; }
public DbSet<Book> Books { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Publisher>().HasKey(p => p.PublisherId);
modelBuilder.Entity<Publisher>().Property(c => c.PublisherId)
.HasDatabaseGeneratedOption(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity);
modelBuilder.Entity<Book>().HasKey(b => b.BookId);
modelBuilder.Entity<Book>().Property(b => b.BookId)
.HasDatabaseGeneratedOption(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity);
modelBuilder.Entity<Book>().HasRequired(p => p.Publisher)
.WithMany(b => b.Books).HasForeignKey(b=>b.PublisherId);
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
}
}
}
Our LibraryContext class that inherits the DbContext class is ready. The LibraryContext class has a three-part constructor, DbSet properties, and an OnModelCreating method. Let's see each one by one.
Constructor: It is an empty constructor that doesn't have any parameters, in other words it is the default constructor but it inherits the base class single string parameterized constructor. This constructor constructs a new context instance using the given string as the name (as we used) or the connection string for the database to which a connection will be made. Here DbConnectionString is the name of the connection string defined in the web.config file of the application.
public LibraryContext(): base("name=DbConnectionString")
{
}
Property: When developing with the Code First workflow you define a derived DbContext that represents the session with the database and exposes a DbSet for each type in your model. The common case shown in the Code First examples is to have a DbContext with public automatic DbSet properties for the entity types of your model.
public DbSet<Publisher> Publishers { get; set; }
public DbSet<Book> Books { get; set; }
The Dbset property represents an entity set used to perform create, read, update, and delete operations. A non-generic version of DbSet<TEntity> can be used when the type of entity is not known at build time. Here we are using the plural name of the property for an entity, that means your table will be created with this name in the database for that specific entity.
Method: The LibraryContext class has an override OnModelCreating method. This method is called when the model for a derived context has been initialized, but before the model has been locked down and used to initialize the context. The default implementation of this method does nothing, but it can be overridden in a derived class such that the model can be further configured before it is locked down. Basically in this method we configure the database table that will be created by a model or a defined relationship among those tables.
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Publisher>().HasKey(p => p.PublisherId);
modelBuilder.Entity<Publisher>().Property(c => c.PublisherId)
.HasDatabaseGeneratedOption(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity);
modelBuilder.Entity<Book>().HasKey(b => b.BookId);
modelBuilder.Entity<Book>().Property(b => b.BookId)
.HasDatabaseGeneratedOption(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity);
modelBuilder.Entity<Book>().HasRequired(p => p.Publisher)
.WithMany(b => b.Books).HasForeignKey(b=>b.PublisherId);
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
}
This method accepts one parameter, an object of DbModelBuilder. This DbModelBuilder class maps POCO classes to database schema. This method is called only once when the first instance of a derived context is created. The model for that context is then cached and is for all further instances of the context in the app domain. This caching can be disabled by setting the ModelCaching property on the given ModelBuidler, but this can seriously degrade performance. More control over caching is provided through use of theDbModelBuilder and DbContext classes directly.
Configure/Mapping Properties with the Fluent API
The OnModelCreating() method under the LibraryContext class uses the Fluent API to map and configure properties in the table. So let's see each method used in the OnModelCreating() method one by one.
modelBuilder.Entity<Book>().HasRequired(p => p.Publisher)
.WithMany(b => b.Books).HasForeignKey(b=>b.PublisherId);
3. Create Controller for CRUD Operations
Now we create two controllers, one for Publisher CRUD operations (PublisherController.cs) and another for Book CRUD operations (BookController.cs) under the Controllers folder in the application. So here is the code for each.
The Publisher controller in the file PublisherController.cs in the Controllers folder:
using System.Linq;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using ExampleCodeFirstApproch.Models;
namespace ExampleCodeFirstApproch.Controllers
{
public class PublisherController : Controller
{
LibraryContext objContext;
public PublisherController()
{
objContext = new LibraryContext();
}
#region List and Details Publisher
public ActionResult Index()
{
var publishers = objContext.Publishers.ToList();
return View(publishers);
}
public ViewResult Details(int id)
{
Publisher publisher =
objContext.Publishers.Where(x=>x.PublisherId==id).SingleOrDefault();
return View(publisher);
}
#endregion
#region Create Publisher
public ActionResult Create()
{
return View(new Publisher());
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult Create(Publisher publish)
{
objContext.Publishers.Add(publish);
objContext.SaveChanges();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
#endregion
#region edit publisher
public ActionResult Edit(int id)
{
Publisher publisher = objContext.Publishers.Where(
x => x.PublisherId == id).SingleOrDefault();
return View(publisher);
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult Edit(Publisher model)
{
Publisher publisher = objContext.Publishers.Where(
x => x.PublisherId == model.PublisherId).SingleOrDefault();
if (publisher != null)
{
objContext.Entry(publisher).CurrentValues.SetValues(model);
objContext.SaveChanges();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
return View(model);
}
#endregion
#region Delete Publisher
public ActionResult Delete(int id)
{
Publisher publisher = objContext.Publishers.Find(id);
return View(publisher);
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult Delete(int id, Publisher model)
{
var publisher =
objContext.Publishers.Where(x => x.PublisherId == id).SingleOrDefault();
if (publisher != null)
{
objContext.Publishers.Remove(publisher);
objContext.SaveChanges();
}
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
#endregion
}
}
The Book controller in the file BookController.cs in the Controllers folder:
using System.Linq;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using ExampleCodeFirstApproch.Models;
namespace ExampleCodeFirstApproch.Controllers
{
public class BookController : Controller
{
LibraryContext objContext;
public BookController()
{
objContext = new LibraryContext();
}
#region List and Details Book
public ActionResult Index()
{
var books = objContext.Books.ToList();
return View(books);
}
public ViewResult Details(int id)
{
Book book = objContext.Books.Where(x=>x.BookId==id).SingleOrDefault();
return View(book);
}
#endregion
#region Create Publisher
public ActionResult Create()
{
return View(new Book());
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult Create(Book book)
{
objContext.Books.Add(book);
objContext.SaveChanges();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
#endregion
#region Edit Book
public ActionResult Edit(int id)
{
Book book = objContext.Books.Where(x => x.BookId == id).SingleOrDefault();
return View(book);
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult Edit(Book model)
{
Book book = objContext.Books.Where(x => x.BookId == model.BookId).SingleOrDefault();
if (book != null)
{
objContext.Entry(book).CurrentValues.SetValues(model);
objContext.SaveChanges();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
return View(model);
}
#endregion
#region Delete Book
public ActionResult Delete(int id)
{
Book book = objContext.Books.Find(id);
return View(book);
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult Delete(int id, Publisher model)
{
var book = objContext.Books.Where(x => x.BookId == id).SingleOrDefault();
if (book != null)
{
objContext.Books.Remove(book);
objContext.SaveChanges();
}
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
#endregion
}
}
Both Publisher and Book controllers are ready and create a view according to the action method using a scaffold template and you can download a zip folder. Run the application and you get that your tables are created in the database with a relationship.