
March 26, 2024 08:05 by
 Peter
PeterMany current software applications rely on background processes or services to complete numerous functions asynchronously without interfering with the user experience. Background services, whether they're processing data, sending emails, or conducting routine maintenance activities, are critical to keeping applications responsive and efficient. Background services in the.NET Core ecosystem make it easy and efficient to implement asynchronous operations.
What are Background Services?
Background services in.NET Core are long-running processes that operate independently of the main application thread. They run in the background and often conduct activities like data processing, monitoring, or periodic actions without interfering with the main application's execution flow. These services are built on the BackgroundService base class supplied by the.NET Core framework, making it easy to manage their lifecycle and execution.
Benefits of Background Services
- Improved Performance: By offloading tasks to background services, the main application thread remains responsive, providing a smoother user experience.
- Scalability: Background services can be scaled independently, allowing applications to handle varying workloads efficiently.
- Asynchronous Processing: Background services enable asynchronous processing of tasks, enabling applications to perform multiple operations concurrently.
- Modular Design: Separating background tasks into services promotes modular and maintainable code, enhancing the overall codebase's readability and manageability.
Implementing Background Services in.NET Core
Let's look at an example to learn how to develop background services in.NET Core.
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using System;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
public class ExampleBackgroundService : BackgroundService
{
private readonly ILogger<ExampleBackgroundService> _logger;
public ExampleBackgroundService(ILogger<ExampleBackgroundService> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
protected override async Task ExecuteAsync(CancellationToken stoppingToken)
{
while (!stoppingToken.IsCancellationRequested)
{
_logger.LogInformation("Background service is running at: {time}", DateTimeOffset.Now);
// Perform your background task here
await Task.Delay(5000, stoppingToken); // Delay for 5 seconds before the next iteration
}
}
}
In this example
- We create a class ExampleBackgroundService that inherits from BackgroundService.
- In the constructor, we inject an instance of ILogger to log messages.
- We override the ExecuteAsync method, where the actual background task logic resides. Inside this method, we have a loop that runs until cancellation is requested.
- Within the loop, we perform the background task, in this case, logging the current time.
- We use Task. Delay to introduce a 5-second delay before the next iteration.
Registering Background Services
To use background services in your .NET Core application, you need to register them with the Dependency Injection container in your Startup. cs file.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddHostedService<ExampleBackgroundService>();
}
Background services in .NET Core offer a powerful mechanism for implementing asynchronous tasks in applications. By leveraging the BackgroundService base class, developers can easily create and manage long-running background tasks, enhancing application responsiveness and scalability. With the provided example and insights, you should now have a solid understanding of how to implement and utilize background services effectively in your .NET Core applications.
European best, cheap and reliable ASP.NET hosting with instant activation. HostForLIFE.eu is #1 Recommended Windows and ASP.NET hosting in European Continent. With 99.99% Uptime Guaranteed of Relibility, Stability and Performace. HostForLIFE.eu security team is constantly monitoring the entire network for unusual behaviour. We deliver hosting solution including Shared hosting, Cloud hosting, Reseller hosting, Dedicated Servers, and IT as Service for companies of all size.


March 19, 2024 08:03 by
 Peter
PeterThe ".NET Framework" and ".NET" (previously known as ".NET Core") are two distinct implementations of the.NET platform, each having a different purpose and addressing various scenarios. However, they share a similar ancestor and are part of the larger.NET ecosystem.
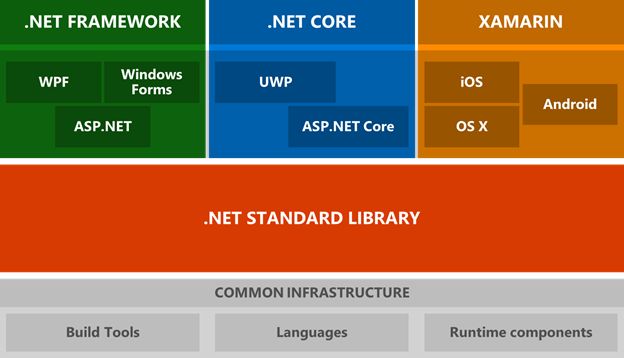
Differences
- .NET Framework: The .NET Framework is the original implementation of the .NET platform, introduced in the early 2000s. It is primarily designed for building Windows-based applications, including desktop applications, web applications, and services. It includes libraries such as Windows Forms, ASP.NET Web Forms, and WPF.
- .NET (formerly .NET Core): .NET (or ".NET 5" and later versions) is a modern, cross-platform implementation of the .NET platform. It is designed to be lightweight, modular, and highly scalable, with support for building applications on Windows, Linux, and macOS. It includes libraries such as ASP.NET Core, Entity Framework Core, and ML.NET.
Evolution: For many years, the.NET Framework served as the platform's foundation. However, as the computing landscape developed, Microsoft introduced.NET Core as a modern, cross-platform alternative to the.NET Framework's restrictions. In November 2020, Microsoft combined.NET Core,.NET Framework, and Xamarin into a single.NET platform dubbed ".NET."
Migration Path: Although.NET Core and.NET Framework have different implementations, Microsoft has given tools and guidelines to help developers move their existing.NET Framework programs to.NET Core and, eventually, to.NET.
European best, cheap and reliable ASP.NET hosting with instant activation. HostForLIFE.eu is #1 Recommended Windows and ASP.NET hosting in European Continent. With 99.99% Uptime Guaranteed of Relibility, Stability and Performace. HostForLIFE.eu security team is constantly monitoring the entire network for unusual behaviour. We deliver hosting solution including Shared hosting, Cloud hosting, Reseller hosting, Dedicated Servers, and IT as Service for companies of all size.


March 14, 2024 07:11 by
 Peter
PeterThe.NET runtime employs IL (Intermediate Language) as a bridging language. It combines all high-level.NET languages into a single language. This is why you can create multilingual applications in.NET. You can write a portion of your program in F# while utilizing an entirely different.NET language for the remainder. Behind the scenes, there is only one language: IL. In our previous tutorial, we talked about the compilation process. It's now time to start creating small programs in the.NET IL language.
Benefits of Learning.NET IL
- Before we begin, let's grasp the importance of learning.NET IL:
- Deeper Understanding: IL can assist you in understanding what happens "under the hood" when you run your.NET software. This can be useful for troubleshooting complex problems or improving performance.
- Specific Tasks: Understanding IL is useful in some sophisticated applications, such as dynamic code generation.
Setting Up the Environment
There is no need to install any specialized programs! You can use a basic text editor such as Notepad++ (but Notepad++ is preferred). Visual Studio lacks a built-in template for writing IL code.
Launch your choice text editor and begin development.
.assembly extern mscorlib {}
.assembly firstILProject {}
.module firstILProject.exe
.class public Program extends [mscorlib]System.Object
{
.method public static void MyMain(string[] args) cil managed
{
.entrypoint
ldstr "Hello from IL code"
call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string)
call string [mscorlib]System.Console::ReadLine()
pop
ret
}
}
Compiling Your Application
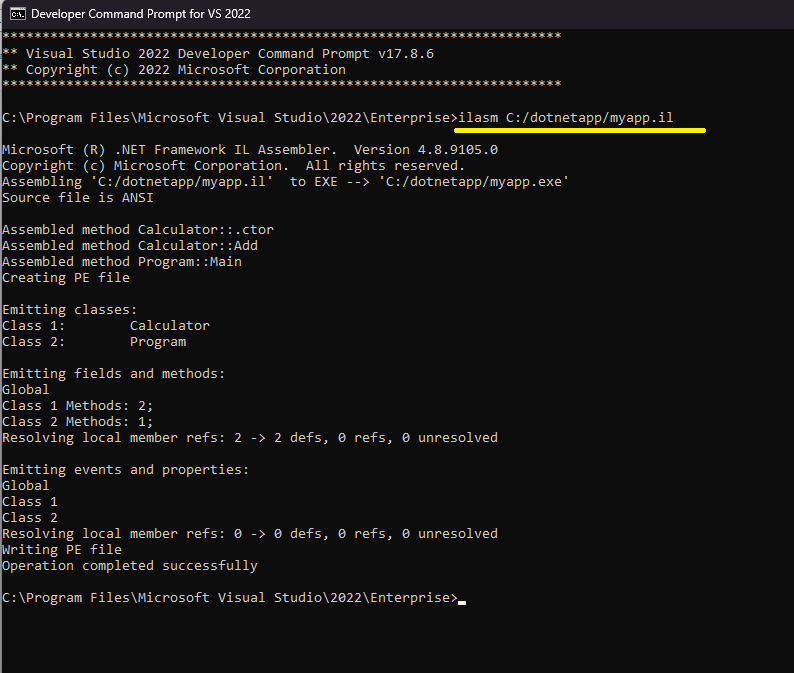
To compile your program, simply save it in any folder with the.il extension. Then, launch the "developer command prompt" and execute ilasm to compile your program.
Developer command prompt for Visual Studio.
Sample Code Structure
Here's a breakdown of a typical IL code structure:
External Reference
.assembly extern mscorlib {}
This line references the external mscorlib library, which provides functionalities your application might need.
Main Assembly
.assembly firstILProject {}
This line defines your application assembly and gives it a unique name (firstILProject in this case).
Module Definition
.module firstILProject.exe
This line defines a module named "firstILProject.exe." A module can represent an executable file (.exe) or a Dynamic-link library (DLL).
Class Definition
.class public extends [System.Object] firstILProject
This line creates a public class named firstILProject that inherits from System.Object (all classes in .NET inherit from System.Object by default).
Entry Point Method
.method static public void Main()
This line declares the Main method, the entry point for your console application.
Stack Operations
method static public void Main()
.entrypoint
ldstr "Hello, World!" // Load string "Hello, World!" onto the stack
call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string) // Call the WriteLine method to print the string
pop // Remove the string from the stack
ret // Return from the method
ldstr: This operator loads a string onto the stack.
call: This keyword is used to call existing methods.
pop: This removes the top element from the stack.
ret: This returns from the current method.
Conclusion
This is a basic overview of writing .NET IL code. By understanding these concepts, you can begin creating simple applications and delve deeper into the world of .NET internals.
European best, cheap and reliable ASP.NET hosting with instant activation. HostForLIFE.eu is #1 Recommended Windows and ASP.NET hosting in European Continent. With 99.99% Uptime Guaranteed of Relibility, Stability and Performace. HostForLIFE.eu security team is constantly monitoring the entire network for unusual behaviour. We deliver hosting solution including Shared hosting, Cloud hosting, Reseller hosting, Dedicated Servers, and IT as Service for companies of all size.


March 8, 2024 07:34 by
 Peter
PeterRate limitation is an important feature of web application security and performance management since it helps to prevent misuse and guarantee that resources are used fairly. In ASP.NET Core, rate restriction can be implemented using middleware, which provides a centralized way for controlling the rate of incoming requests. This blog discusses rate-limiting middleware, its implementation in ASP.NET Core, and its importance in online application development.
What is Rate Limiting?
Rate limitation is a mechanism that limits the amount of requests a client can make to a web server during a given time period. It aids in the prevention of misuse, protects against denial-of-service (DoS) assaults, and ensures equal resource access.
Rate-Limiting Middleware for ASP.NET Core
The rate-limiting middleware in ASP.NET Core intercepts incoming requests and enforces rate limitations based on predefined constraints. It lies between the client and the application, monitoring request rates and returning appropriate HTTP status codes when limitations are reached.
1. Install Required Packages
Install the AspNetCoreRateLimit package from NuGet:
dotnet add package AspNetCoreRateLimit
2. Configure Rate-Limiting Middleware
In the Startup.cs file, add the rate-limiting middleware to the request processing pipeline:
using AspNetCoreRateLimit;
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
// Other middleware configurations
app.UseIpRateLimiting();
app.UseClientRateLimiting();
}
3. Configure Rate-Limiting Options
Configure rate-limiting options in the appsettings.json file:
{
"IpRateLimiting": {
"EnableEndpointRateLimiting": true,
"StackBlockedRequests": true,
"RealIpHeader": "X-Real-IP",
"HttpStatusCode": 429,
"QuotaExceededResponse": {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Content": "{\"error\": \"Rate limit exceeded\"}"
},
"GeneralRules": [
{
"Endpoint": "*",
"Period": "1s",
"Limit": 5
}
]
},
"ClientRateLimiting": {
"EnableEndpointRateLimiting": true,
"StackBlockedRequests": true,
"HttpStatusCode": 429,
"QuotaExceededResponse": {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Content": "{\"error\": \"Rate limit exceeded\"}"
},
"GeneralRules": [
{
"Endpoint": "*",
"Period": "1s",
"Limit": 100
}
]
}
}
4. Test Rate Limiting
Test the rate-limiting middleware by sending requests to your ASP.NET Core application and observing the behavior when rate limits are exceeded.
Rate-limiting middleware in ASP.NET Core is a useful tool for controlling request rates and protecting online applications from misuse and overload. Rate limitation allows developers to improve the security, stability, and performance of their ASP.NET Core apps while also assuring fair and equitable access to resources for all users. Accept rate restriction as an essential component of web application development to protect your apps from malicious actions and resource depletion threats.
Conclusion
Rate-limiting middleware in ASP.NET Core is a useful tool for controlling request rates and protecting online applications from misuse and overload. Rate limitation allows developers to improve the security, stability, and performance of their ASP.NET Core apps while also assuring fair and equitable access to resources for all users. Accept rate restriction as an essential component of web application development to protect your apps from malicious actions and resource depletion threats.
Happy coding!
European best, cheap and reliable ASP.NET hosting with instant activation. HostForLIFE.eu is #1 Recommended Windows and ASP.NET hosting in European Continent. With 99.99% Uptime Guaranteed of Relibility, Stability and Performace. HostForLIFE.eu security team is constantly monitoring the entire network for unusual behaviour. We deliver hosting solution including Shared hosting, Cloud hosting, Reseller hosting, Dedicated Servers, and IT as Service for companies of all size.


March 5, 2024 06:32 by
 Peter
PeterData structures are at the foundation of software development, determining how information is organized, stored, and manipulated within applications. Developers in the.NET environment have access to a wide range of data structures that allow for efficient data management, resulting in strong and scalable software solutions. In this post, we will look at some key.NET data structures with practical examples, providing light on their uses and benefits.
1. Lists (.NET Dynamic Arrays)
Lists are dynamic arrays in.NET that allow for size flexibility and easy manipulation. Consider the following scenario: we need to keep track of the names of all our students.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
List<string> students = new List<string>();
// Adding students to the list
students.Add("Alice");
students.Add("Bob");
students.Add("Charlie");
// Iterating over the list
foreach (var student in students)
{
Console.WriteLine(student);
}
}
}
2. Queues (FIFO Principle)
Queues follow the First-In-First-Out (FIFO) principle, commonly used in task scheduling or message processing scenarios. Let's simulate a simple printing queue.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Queue<string> printQueue = new Queue<string>();
// Enqueueing documents to be printed
printQueue.Enqueue("Document1");
printQueue.Enqueue("Document2");
printQueue.Enqueue("Document3");
// Printing documents in the order they were added
while (printQueue.Count > 0)
{
string document = printQueue.Dequeue();
Console.WriteLine("Printing: " + document);
}
}
}
3. Stacks (LIFO Principle)
Stacks adhere to the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) principle and are commonly used in situations like expression evaluation or browser history. Let's implement a simple browser history using a stack.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Stack<string> browserHistory = new Stack<string>();
// Navigating through web pages
browserHistory.Push("Homepage");
browserHistory.Push("About");
browserHistory.Push("Contact");
// Navigating back through history
while (browserHistory.Count > 0)
{
string currentPage = browserHistory.Pop();
Console.WriteLine("Current Page: " + currentPage);
}
}
}
4. Dictionaries (Key-Value Pairs)
Dictionaries in .NET store key-value pairs, enabling efficient lookup and retrieval based on keys. Let's create a simple dictionary to store the ages of individuals.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Dictionary<string, int> ages = new Dictionary<string, int>();
// Adding individuals and their ages
ages["Alice"] = 25;
ages["Bob"] = 30;
ages["Charlie"] = 35;
// Retrieving ages
Console.WriteLine("Bob's age: " + ages["Bob"]);
}
}
Conclusion
Understanding and utilizing.NET data structures is critical for effective program development. Developers can create more robust and scalable apps by learning about these data structures and their uses through real examples. Whether you're managing collections, creating algorithms, or improving performance, a good understanding of.NET data structures gives you the confidence to take on a variety of programming issues.
European best, cheap and reliable ASP.NET hosting with instant activation. HostForLIFE.eu is #1 Recommended Windows and ASP.NET hosting in European Continent. With 99.99% Uptime Guaranteed of Relibility, Stability and Performace. HostForLIFE.eu security team is constantly monitoring the entire network for unusual behaviour. We deliver hosting solution including Shared hosting, Cloud hosting, Reseller hosting, Dedicated Servers, and IT as Service for companies of all size.
