The JSON format is syntactically identical to the code for creating JavaScript objects. Because of this similarity, instead of using a parser (like XML does), a JavaScript program can use standard JavaScript functions to convert JSON data into native JavaScript objects.

Much Like XML Because
- Both JSON and XML is "self describing" (human readable)
- Both JSON and XML is hierarchical (values within values)
- Both JSON and XML can be parsed and used by lots of programming languages
- Both JSON and XML can be fetched with an XMLHttpRequest
Much Unlike XML Because
- JSON doesn't use end tag
- JSON is shorter
- JSON is quicker to read and write
- JSON can use arrays
The biggest difference is:
XML has to be parsed with an XML parser, JSON can be parsed by a standard JavaScript function.
Visual Studio 2015 with ASP.NET 5 is a sweet surprise for developers. ASP.NET 5 has various JSON files to play with. These files handles global settings for solution, project specific settings, client side packages and node modules packages. In the post, we will take a close look at every JSON file and its code.
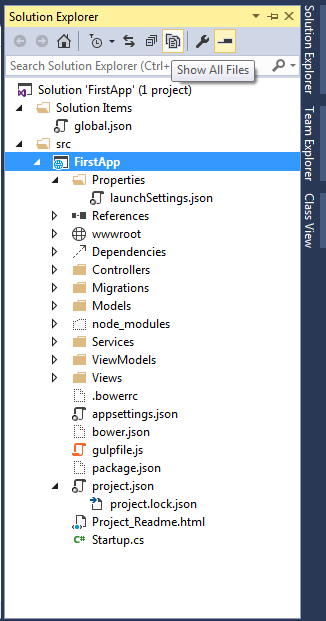
As seen from the above image, there are mainly 6 configuration json files.
- Global.json
- appsetting.json
- Project.json
- launchsetting.json
- bower.json
- package.json
- hosting.json: Though this file is not present in solution explorer till RC 1 release but you can add it manually.
Global.json
As the name suggests, the settings defined in the file should work for the solution as whole. The settings defined in global.json implies to all the projects in the solution. If you open the file, by default you will see the following code.
{
"projects": [ "src", "test" ],
"sdk": {
"version": "1.0.0-rc1-update1"
}
}
The projects property defines the locations of your solution’s source code. VS 2015, specifies two location for projects in the solution src and test. While the src contains the actual application and test project contains any test (if you have selected option of creating test project while creating the solution for first time].
The team has also made a very interesting and useful change. If you recollect, when you build your application, then all your .dll are placed in bin directory in the same path, where your project is. And we have to handle bin folder very carefully while check-in the code in source control and at the time of deployment. But good news is that it is moved to another location. So you don’t have to worry now. The build artifact is now placed in “Artifact” folder (at the same location), which makes life easy while excluding things from source control.
And the second property sdk specifies the version of the DNX (.Net Execution Environment) that Visual Studio will use when opening the solution. Specifying the version has an advantage as while working on multiple projects, you can target different versions of ASP.NET 5.
appsettings.json
appsettings.json file is used to define application related settings like connection string, logging settings, or any other custom key which we used to define in web.config file.
{
"Data": {
"DefaultConnection": {
"ConnectionString": "Server=(localdb)\\mssqllocaldb;Database=aspnet5-FirstApp-0ed2f710-6535-4c4e-b080-c26601fbb414;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true"
}
},
"Logging": {
"IncludeScopes": false,
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Verbose",
"System": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Information"
}
}
}
Project.json
This file is used to define project settings and server side dependencies. It largely replaces the web.config file from previous versions of ASP.NET. Read “What is Project.json in ASP.NET 5 (vNext)”. Few things have changed in ASP.NET 5 RC1 release for project.json file.
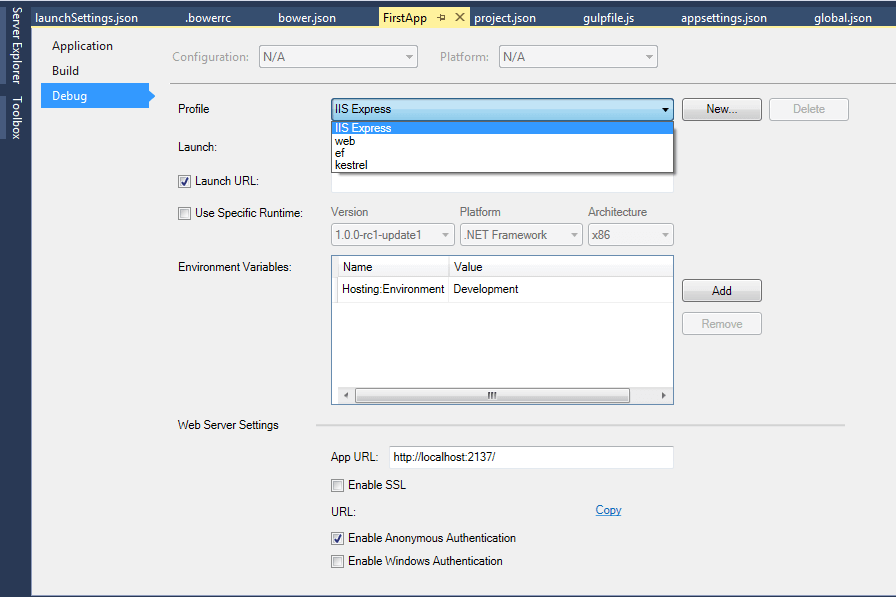
launchSetting.json
This json file holds project specific settings associated with each profile Visual Studio is configured to use to launch the application, including any environment variables that should be used. You can define framework for your project for compliation and debugging for specific profiles.
{
"iisSettings": {
"windowsAuthentication": false,
"anonymousAuthentication": true,
"iisExpress": {
"applicationUrl": "http://localhost:2137/",
"sslPort": 0
}
},
"profiles": {
"IIS Express": {
"commandName": "IISExpress",
"launchBrowser": true,
"environmentVariables": {
"Hosting:Environment": "Development"
}
},
"web": {
"commandName": "web",
"environmentVariables": {
"Hosting:Environment": "Development"
},
"sdkVersion": "dnx-clr-win-x86.1.0.0-rc1-update1"
},
"kestrel": {
"commandName": "kestrel",
"sdkVersion": "dnx-clr-win-x86.1.0.0-rc1-update1"
}
}
}
ASP.NET 5 ships with support for 3 different servers:
- Microsoft.AspNet.Server.IIS
- Microsoft.AspNet.Server.WebListener (WebListener)
- Microsoft.AspNet.Server.Kestrel (Kestrel)
So by default, there will be 3 different profiles. However, it also depends on the commands section of project.json. You can change settings for each profile via right click on the Project and then select properties. Read detailed post about launchsetting.json in ASP.NET 5
Bower.json
Bower is a package manager for the web. Bower can manage components that contain HTML, CSS, JavaScript, fonts or even image files. Bower doesn’t concatenate or minify code or do anything else – it just installs the right versions of the packages you need and their dependencies. With ASP.NET 5 web projects jQuery and bootstrap packages are already installed and bower, gulp and NPM are already in place.
Client-side packages are listed in the bower.json file. As mentioned earlier, bootstrap, jQuery and jQuery validation are pre-configured with ASP.NET 5 project templates.
{
"name": "ASP.NET",
"private": true,
"dependencies": {
"bootstrap": "3.3.5",
"jquery": "2.1.4",
"jquery-validation": "1.14.0",
"jquery-validation-unobtrusive": "3.2.4"
}
}
Visual Studio watches the bower.json file for changes. Upon saving, the bower install command is executed. There is another file named “ .bowerrc” which defines the location at which bower package needs to be installed. Open it, and notice that the directory property is set to “wwwroot/lib”.
Package.json
npm is another package manager like bower. But npm is used for installing Node js modules where bower is used for managing front end components like html, css, js, etc. As mentioned earlier, the ASP.NET 5 project template pre-configures NPM, Gulp and bower. Gulp is JavaScript task runner which is used to automate various tasks like minification and bundling of js and css, checking errors in js etc… Since Gulp is a node.js module so npm is used. So node.js modules are listed in package.json.\
{
"name": "ASP.NET",
"version": "0.0.0",
"devDependencies": {
"gulp": "3.8.11",
"gulp-concat": "2.5.2",
"gulp-cssmin": "0.1.7",
"gulp-uglify": "1.2.0",
"rimraf": "2.2.8"
}
}
You can see the installed bower and npm modules by expanding src -> dependencies option.
HostForLIFE.eu ASP.NET 5 Hosting
European best, cheap and reliable ASP.NET hosting with instant activation. HostForLIFE.eu is #1 Recommended Windows and ASP.NET hosting in European Continent. With 99.99% Uptime Guaranteed of Relibility, Stability and Performace. HostForLIFE.eu security team is constantly monitoring the entire network for unusual behaviour. We deliver hosting solution including Shared hosting, Cloud hosting, Reseller hosting, Dedicated Servers, and IT as Service for companies of all size.
