This article will explain the SOLID principles, which one of those acronyms means alongside a practical example of an architectural problem that we could use in order to fix the problem.
What are the SOLID principles?
A SOLID principle is a group of 5 different design patterns whose main focus is to create loosely coupled architectures with a high level of maintainability. The name SOLID comes from the acronym of its five principles,
S - Single Responsability Principle;
O - Open-Closed Principle;
L - Liskov Substitution Principle;
I - Interface Segregation Principle;
D - Dependency Inversion Principle.
If in your project you have the common problem to solve a bug and create two different bugs then you must start to think about using the SOLID principles in order to have a cleaner and more organized code, which does not break other features when you are working in a specific feature.
S - SRP - Single Responsibility Principle
“A class should have one, and only one, a reason to change.” (Robert C. Martin)
Avoiding Jack of all Trades' classes, the Single Responsibility Principle says that your class should have a single responsibility. This means that you should avoid, at all costs, having classes with multiple functionalities.
Imagine doing maintenance in a class with multiples functionalities, the risk of fixing one functionality but breaking other functionalities as a side-effect is extremely high. To overcome those kinds of situations you should apply the Single Responsibility Principle.
One great example of the Single Responsibility Principle being applied is the 3-tier projects architectures, where each tier is responsible only for their tasks. Ie.: the business layer is responsible to validate business logics where the repository layer is responsible to manipulate the database.
O - OCP - Open/Closed Principle
“A class is closed, since it may be compiled, stored in a library, baselined, and used by client classes. But it is also open, since any new class may use it as parent, adding new features. When a descendant class is defined, there is no need to change the original or to disturb its clients.” (Bertrand Meyer)
The topic here is also to avoid Jack of All Trades' classes but in a different manner. The open-closed says that instead of modifying your base classes to add more features you should create a new class with those features, and this class will be inheriting the base class.
Imagine having a class that based on the input could go through one workflow or another workflow completely different, you will probably manage that with conditional statements.
Now, imagine when you need to do maintenance in one of those workflows. What is the risk of breaking, by mistake, the other ones?
The Open-Closed Principle says that you must have a base class that should not be modified to add new functionalities. Instead, you should have a new class inheriting the base class with those new functionalities. In this case, when you need to do maintenance in a specific workflow you are certain that will have no side effects in the others workflows.
L - LSP - Liskov Substitution Principle
“Subtypes must be substitutable for their base types.” (Barbara Liskov)
The main point from the Liskov Substitution Principle is to create a base class in order to be inherited from its subtypes.
The Liskov Substitution Principle states that if we change our class for its base class we should not have different behaviour. Instead, if we change our subclasses by our base class without breaking the application because our base classes must behave in the same way as our subclasses. In this case, if we need to replace our subclasses for another subclass we would not need to refactor anything because it would be a simple substitution and everything would still be working the same.
I - ISP - Interface Segregation Principle
“No client should be forced to depend on methods it does not use.” (Robert C. Martin)
This principle is not the best friend of laziness, it is the worst friend of those projects when you place all your needed contracts in a single place, with this we are not going to be able to reuse those interfaces or, even worse, we will not be using every method in the contract. Instead of creating an interface with many contracts on it, you should create as many interfaces as possible by grouping common behaviours.
The Interface Segregation Principle says that we should segregate interfaces in order to do not depend on interfaces with a contract that will not be implemented. We should have smaller interfaces and depend on more than one interface if needed.
D - DIP - Dependency Inversion Principle
“High-level modules should not depend upon low-level modules. Both should depend upon abstractions” (Robert C. Martin)
Here we have the best friend of loosely coupled applications and unit testing. If you have ever needed to replace one dependency and to do this you had to refactor every method that this dependency was being called then you should use the Dependency Inversion Principle.
The Dependency Inversion Principle says that our classes should not depend on low-level modules because this created a strong coupled application, making it very difficult to unit test and substitute dependencies. Instead, our classes should receive in their constructor the abstraction of their low-level dependencies, with this we may change our classes that implement the contract without breaking or needing to refactor the whole application. Also, we could easily mock our dependencies in order to create unit tests.
SOLID principles Practical Usage One-by-One
SRP - The Problem - Class that sum two numbers and log it
Here we have a problem that we can use the Single Responsability Principle to fix it. A class with two functionalities, the first is to sum two numbers and the second is to log this operation
class Problem
{
public int Sum(int numberOne, int numberTwo)
{
int result = numberOne + numberTwo;
LogCalculations("Sum Operation. Number one: " + numberOne + ", Number two: " + numberTwo + ". Result: " + result);
return result;
}
private void LogCalculations(string message)
{
string path = Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.Desktop) + @"\log.txt";
using (StreamWriter sw = File.CreateText(path))
{
sw.WriteLine(message);
}
}
}
Applying the Single Responsibility Principle we would have two different classes:
class Solution
{
public int Sum(int numberOne, int numberTwo)
{
int result = numberOne + numberTwo;
Logging.Log("Sum Operation. Number one: " + numberOne + ", Number two: " + numberTwo + ". Result: " + result);
return result;
}
}
public static class Logging
{
public static void Log(string message)
{
string path = Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.Desktop) + @"\log.txt";
using (StreamWriter sw = File.CreateText(path))
{
sw.WriteLine(message);
}
}
}
OCP - The Problem 1 - Class to do math calculations
In this class, we receive as input one enumeration with the operation type and return the result from this operation. If we need to add or modify one operation, we would need to modify the class.
public class MathCalculate
{
public double Calculate(double numberA, double numberB, CalculationType calculationType)
{
double result = 0;
switch (calculationType)
{
case CalculationType.addition:
result = numberA + numberB;
break;
case CalculationType.multiplication:
result = numberA * numberB;
break;
case CalculationType.subtraction:
result = numberA - numberB;
break;
default:
break;
}
return result;
}
}
public enum CalculationType
{
addition,
multiplication,
subtraction
}
Applying the Open-Closed Principle we would have a base class "Calculation" and each operation would be a new class, inheriting from this base class. If we need to add or modify a new operation, then we would need to work only in the class of this operation
public abstract class BaseCalculation
{
public abstract double Calculate(double numberA, double numberB);
}
public class AdditionCalculation : BaseCalculation
{
public override double Calculate(double numberA, double numberB)
{
return numberA + numberB;
}
}
public class MultiplicationCalculation : BaseCalculation
{
public override double Calculate(double numberA, double numberB)
{
return numberA * numberB;
}
}
public class SubtractionCalculation : BaseCalculation
{
public override double Calculate(double numberA, double numberB)
{
return numberA - numberB;
}
}
public class DivisionCalculation : BaseCalculation
{
public override double Calculate(double numberA, double numberB)
{
return numberA / numberB;
}
}
OCP - The Problem 2 - Email sender with validations
If we need to add or modify the validations, we would need to modify the email sender class, risking to break the email sender functionality.
public class MailSender
{
public void SendMail(string subject, string body, string recipient)
{
SmtpClient smtpClient = new SmtpClient("smtp.gmail.com")
{
Port = 587,
Credentials = new NetworkCredential("email", "password"),
EnableSsl = true,
};
//validate recipient's domain
if (!recipient.ToString().EndsWith("@hostforlifeasp.net"))
{
Console.WriteLine("Mail destinatary not in the domain");
return;
}
//validate body
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(body))
{
Console.WriteLine("Mail body is empty.");
return;
}
smtpClient.SendAsync("[email protected]", recipient, subject, body, null);
}
}
Applying the open-closed principle to solve this problem we would have this email sender class receiving a list of validations. When we need to add or modify one of those validations would not be necessary to update the mail sender class:
public class MailClass
{
public string Subject { get; set; }
public string Body { get; set; }
public string Recipient { get; set; }
}
public interface IValidation<T>
{
bool Validate(T mail);
}
public class DomainValidation : IValidation<MailClass>
{
public bool Validate(MailClass mail)
{
if (mail.Recipient.ToString().EndsWith("@hostforlifeasp.net"))
return false;
return true;
}
}
public class BodyValidation : IValidation<MailClass>
{
public bool Validate(MailClass mail)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(mail.Body))
return false;
return true;
}
}
public class Main
{
public void SendMail(MailClass mailClass, List<IValidation<MailClass>> validations)
{
List<bool> validationsResult = new List<bool>();
validations.ForEach(x => validationsResult.Add(x.Validate(mailClass)));
if (!validationsResult.Any(x => !x))
{
SmtpClient smtpClient = new SmtpClient("smtp.gmail.com")
{
Port = 587,
Credentials = new NetworkCredential("email", "password"),
EnableSsl = true,
};
smtpClient.SendAsync("[email protected]", mailClass.Recipient, mailClass.Subject, mailClass.Body, null);
};
}
}
OCP - Extension Methods
We can also make usage of extension methods in order to extend objects without modifying their base behaviour. The following code extends the String object, adding this new method on it:
public static class SolutionThree
{
public static string PeterString(this string normalString)
{
return "peter's String is: " + normalString;
}
}
LSP - The Problem - Having a subtraction class inheriting from an addition class
In this example, we have an addition class working fine and then we extended it, wrongly, creating the subtraction class. If we replace the subtraction class with the base class (addition) our output will differ.
public class AdditionCalculation
{
public AdditionCalculation(int numberA, int numberB)
{
this.NumberB = numberB;
this.NumberA = numberA;
}
public int NumberA { get; set; }
public int NumberB { get; set; }
public virtual int Calculate()
{
return this.NumberA + NumberB;
}
}
public class SubtractionCalculation : AdditionCalculation
{
public SubtractionCalculation(int numberA, int numberB) : base(numberA, numberB)
{
}
public new int Calculate()
{
return NumberA - NumberB;
}
}
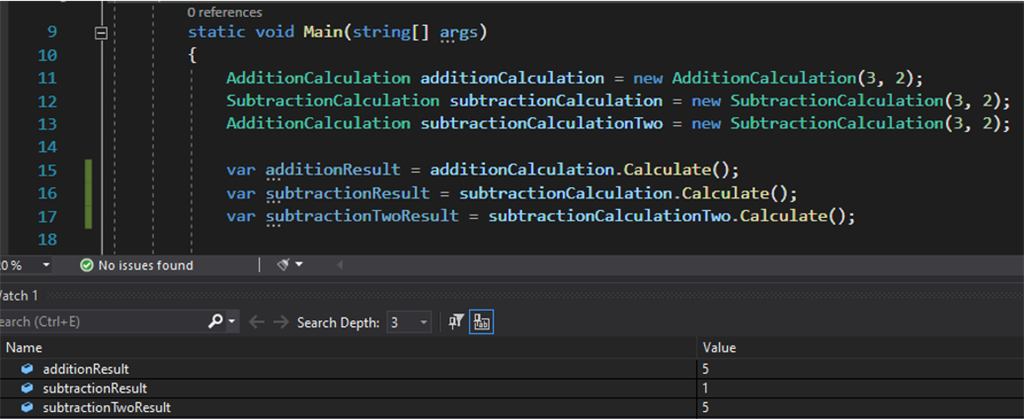
LSP - The Problem - Having a subtraction class inheriting from an addition class
In this example, we have an addition class working fine and then we extended it, wrongly, creating the subtraction class. If we replace the subtraction class with the base class (addition) our output will differ.
public class AdditionCalculation
{
public AdditionCalculation(int numberA, int numberB)
{
this.NumberB = numberB;
this.NumberA = numberA;
}
public int NumberA { get; set; }
public int NumberB { get; set; }
public virtual int Calculate()
{
return this.NumberA + NumberB;
}
}
public class SubtractionCalculation : AdditionCalculation
{
public SubtractionCalculation(int numberA, int numberB) : base(numberA, numberB)
{
}
public new int Calculate()
{
return NumberA - NumberB;
}
}

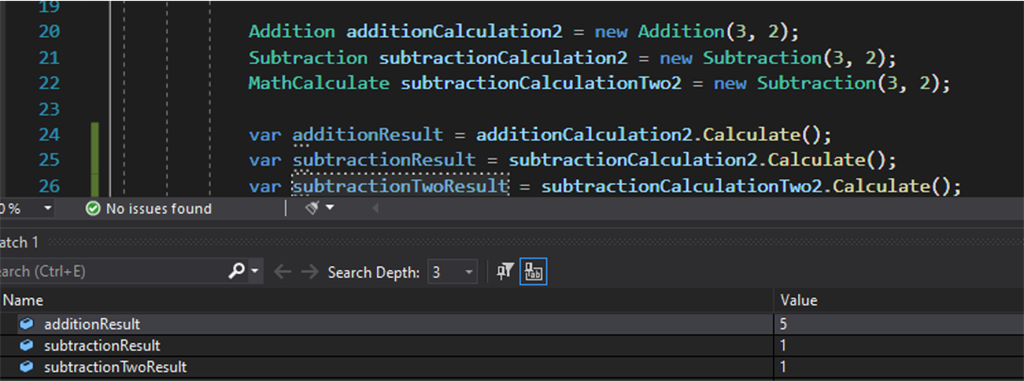
Applying the Liskov Substitution Principle to solve this problem we have a base class then we have the addition and subtraction classes inheriting from this base class. If we change our class with the base class our output is not going to be affected.
public abstract class MathCalculate
{
public MathCalculate(int numberA, int numberB)
{
this.NumberB = numberB;
this.NumberA = numberA;
}
public int NumberA { get; set; }
public int NumberB { get; set; }
public abstract int Calculate();
}
public class Addition : MathCalculate
{
public Addition(int numberA, int numberB) : base(numberA, numberB)
{
}
public override int Calculate()
{
return this.NumberA + NumberB;
}
}
public class Subtraction : MathCalculate
{
public Subtraction(int numberA, int numberB) : base(numberA, numberB)
{
}
public override int Calculate()
{
return NumberA - NumberB;
}
}
ISP - The Problem - A single interface for many type of classes
In this example, we have a single interface called IAnimal that is used for both Human and Whale classes. The problem is that not the whole contract fit both items because, as we all know, whales do not walk.
public interface IAnimal
{
void Walk();
void Breath();
void Eat();
void Argument();
}
public class Human : IAnimal
{
public void Argument()
{
// Argumentation
}
public void Breath()
{
// Breathing
}
public void Eat()
{
// Eating
}
public void Walk()
{
// Walk
}
}
public class Whale : IAnimal
{
public void Argument()
{
// Argumentation
}
public void Breath()
{
// Breathing
}
public void Eat()
{
// Eating
}
public void Walk()
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
Applying the Interface Segregation Principle we break the single interface in smaller interfaces with common methods and then we only use the interfaces that we need in our classes.
public interface IFeed {
void Eat();
}
public interface IArgument
{
void Argument();
}
public interface IGroundMoviment
{
void Walk();
}
public interface IAirMoviment
{
void Fly();
}
public interface IWaterMoviment
{
void Swimm();
}
public class Human : IGroundMoviment, IArgument, IFeed
{
public void Argument()
{
// Argument
}
public void Eat()
{
// Eat
}
public void Walk()
{
// Walk
}
}
public class Whale : IWaterMoviment, IFeed
{
public void Eat()
{
// Eat
}
public void Swimm()
{
// Swimm
}
}
DIP - The Problem - Strong Coupled Application
In this example, we need to instantiate our dependency inside our method, creating a strong coupled application. If we want to replace this dependency we would need a lot of work, needing to change those dependencies at every method that is being used. Also, it is much more difficult to unit test this layer because it is much harder to mock this dependency.
public class BusinessLayer
{
public void AddItem(int itemId)
{
RepositoryLayer repositoryLayer = new RepositoryLayer();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(repositoryLayer.GetItem(itemId)))
repositoryLayer.Update();
else
repositoryLayer.Create();
}
}
public class RepositoryLayer
{
public void Create()
{
//save data into the Database
}
public void Delete()
{
//delete data from the Database
}
public void Update()
{
//update data in the Database
}
public string GetItem(int itemId)
{
//get item from the Database
return "item";
}
}
Applying the Dependency Inversion Principle, we receive the interface of our dependency in the class constructor. If we need to change the class that implements this dependency contract it would not be necessary to refactor any method where we use this dependency.
public class BusinessLayer
{
private readonly IRepositoryLayer repositoryLayer;
public BusinessLayer(IRepositoryLayer repositoryLayer)
{
this.repositoryLayer = repositoryLayer;
}
public void AddItem(int itemId)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(repositoryLayer.GetItem(itemId)))
repositoryLayer.Update();
else
repositoryLayer.Create();
}
}
public interface IRepositoryLayer
{
void Create();
void Delete();
void Update();
string GetItem(int itemId);
}